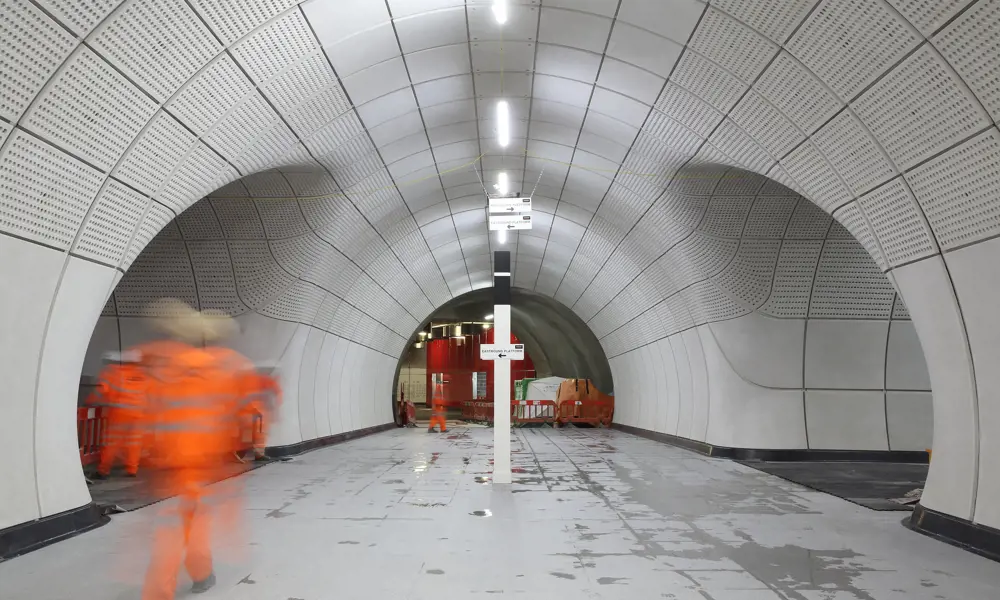
Implementing ground support systems in underground excavations requires careful consideration of geological conditions and stress distributions. Primary support elements typically include rock bolts, cable anchors, and shotcrete applications that work together to maintain tunnel stability. Rock mass classification systems guide the selection of support patterns, while real-time monitoring helps verify system performance. Engineers must account for varying ground conditions, stress redistribution patterns, and potential failure mechanisms when designing support layouts that ensure both immediate and long-term stability of underground openings.
Rock mass behavior
The interaction between reinforcement systems and the surrounding rock mass determines the overall stability of underground openings. Natural joint patterns, rock strength properties, and in-situ stress conditions influence how the ground responds to excavation. Understanding these behaviours helps engineers design appropriate support systems that complement natural rock mass strength while preventing unwanted deformation. The reinforcement strategy must address immediate support requirements and long-term stability concerns as ground conditions evolve.
Steel support systems
Steel supports are crucial in maintaining underground stability through various forms, including steel sets, lattice girders, and specialized profiles. These elements provide immediate support after excavation and work with other reinforcement components. The spacing, size, and configuration of steel supports depend on ground conditions and loading requirements. Engineers must consider rock mass quality, excavation size, and construction sequence when designing steel support systems that effectively control ground deformation.
Shotcrete applications
Shotcrete applications provide essential surface support in underground excavations, creating a protective layer that prevents rock deterioration and maintains stability. The thickness and reinforcement of shotcrete layers vary based on ground conditions and support requirements. Fibre-reinforced shotcrete enhances performance through improved tensile strength and crack control properties. The timing and sequence of shotcrete application significantly influence its effectiveness in controlling ground behaviour and maintaining excavation stability.
Cable bolt systems
Cable bolting systems extend reinforcement capabilities beyond conventional rock bolts, particularly in areas requiring longer anchorage lengths or higher capacity support. These systems support large underground openings and critical intersections where traditional bolting patterns may prove insufficient. The design of cable bolt patterns considers factors such as rock mass structure, stress conditions, and excavation geometry to provide optimal support coverage and load capacity for specific ground conditions.
Grouting techniques
Ground improvement through grouting techniques strengthens weak zones and reduces water inflow in underground excavations. Various grouting methods address ground conditions and project requirements, including cement-based and chemical grouts. The selection of grouting materials and injection patterns depends on joint characteristics, groundwater conditions, and required strength improvement. Proper implementation of grouting programs helps stabilize ground conditions before and during excavation activities.
Support sequence design
The timing and sequence of reinforcement installation significantly influence support system effectiveness. Primary support must be installed promptly after excavation to prevent ground relaxation and maintain stability. Secondary support elements provide additional capacity and long-term protection as needed. The design of installation sequences considers factors such as ground stand-up time, construction logistics, and equipment access to ensure timely and effective support implementation throughout the excavation process.
Monitoring implementation
Regular monitoring of reinforcement performance ensures support systems function as intended and maintain underground stability. Instrumentation programs track ground movement, support loads, and other relevant parameters throughout construction. Monitoring systems help identify potential problems before they become major problems. Implementing comprehensive monitoring programs provides essential feedback for optimizing support designs and maintaining safe working conditions.
The stability of underground excavations depends on properly designed and implemented reinforcement systems that work in harmony with natural ground conditions. Achieving optimal results in Tunneling and mining solutions involves selecting appropriate support systems tailored to specific ground conditions. Through continued advancement in support technologies and installation methods, the industry maintains its ability to develop underground spaces safely and efficiently, supporting the growth of infrastructure and resource development projects worldwide.












